Naming Organic Compounds
Here is an overview of what we will be discussing in this article.
Terminologies used in this article and its meaning
Now, let's discuss the Basic rules in naming organic compounds:
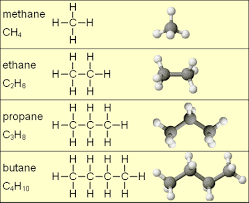
1. Identify the number of carbon atom present in the molecular structure
For you to know the number of carbon atom in the molecular structure of a given organic compound, you must first draft out the structure from the structural formular that is given to you, but if you are given the molecular structure, skip drawing the structure and just go ahead to count the number of carbon atom present in the compound. Once the number of carbon atom present in the compound is known, you should write it down as follows; if there is 1 number of carbon atom, then you name it2. Check for unsaturation
If it is an unsaturated organic compound i.e. having double or triple bonds, you'll have to count from the side having lesser number of carbon atom. For example, C-C-C=C-C, you'll have to count from the right to left because counting from the right to left, we have 2 carbon atom but counting from left to right, we have 3 carbon atom, so you must count from the side that has lesser number of carbon atom (which will be counting from right to left). Keep this noted while we move to the next step...3. Check for functional group
If there is a functional group e.g hydroxyl group(OH), you must count from the last end of carbon atom closest to the functional group. But if there is double or triple bond, do not count from the functional group but from the side that has the lesser number of carbon atom close to the double or triple bond(follow the second step). Also, functional group such as hydroxyl -OH will be abbreviated to give OL which will be added as a suffix while naming the compound.For example C-C-C-C-C-OH will be named pentanol, C-C-C-OH will be named propanol etc.4. Identify the family or series it belongs to
If it is a single bonded compound, it is an alkane(ane), if it has double bond in it's structure, it is an alkene(ene), if it has triple bond, it is an alkyne(yne). All those abbreviations in the brackets is what must be added as the suffix while naming the compound dpepending on the serie the given compound belongs to. An alkane, "ane" will be added as suffix, alkene "ene" will be added as suffix, alkyne "yne" will be added as suffix. Please take note. For example; C=C-C-C, ene must be added as the suffix while naming this compound because it has a double bond hence, it belongs to the alkene serie.If the compound has a functional group attached to it, the functional group abbr. will be added to the series abbr. while naming. e.g C-C-C-OH will be named propanol, C-C=C-OH will be named propenol etc.
5. Find the longest carbon chain
This is self explanatory, all you have to do is to count correctly and find the longest carbon chain. Any compound left out of the chain will surely be an alkyl group(CnH2n+1) and must be given reference while naming. Mostly methyl(CH3) and ethyl(C2H5).For example:Putting it all together
I hope you now know the rules involved in naming organic compounds. So, let's see how everything work while naming an organic compound.If it has a single bond, you should have this(3-methyl butane). But, if a group like hydroxyl, carbonyl,carboxyl etc is attached to it, you should name it as this (3-methyl butanol, 3-methyl butanone, 3-methyl butanoic).
Also, we may have two or more alkyl group. For example, we have a methyl group attached to the 2nd, 3rd and 4th carbon atom, the prefix should be named 2,3,4- trimethyl.. using the example above, you should have 2,3,4- trimethyl butanol.
I hope you understood this, if not please feel free to contact me or ask your questions using the comment box.



Comments
Post a Comment